
2026 How to Select the Best CNC Steel Machining Techniques?
In today's manufacturing landscape, selecting the best CNC steel machining techniques is crucial. The global CNC machining market is expected to reach $100 billion by 2026, highlighting its significance. Companies must focus on precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness to remain competitive.
CNC steel machining requires a deep understanding of materials and processes. Steel grades vary widely, affecting machinability and surface finish. Choosing the wrong technique can lead to increased costs and production delays. Reports indicate that improper machining can waste up to 30% of the material used. This inefficiency emphasizes the need for careful selection.
Moreover, advancements in technology offer new CNC steel options. Innovations in tooling and software can enhance overall performance. Yet, reliance on outdated techniques can hinder progress. Companies must continuously evaluate their methods to adapt to industry changes. Embracing new CNC steel machining technologies could significantly impact productivity and quality.
Understanding the Fundamentals of CNC Steel Machining Techniques
CNC steel machining is a critical process in manufacturing. Understanding its fundamentals is essential for selecting the best techniques. CNC machining uses computerized controls to manage cutting tools. This ensures precision and consistency, important in industries such as aerospace and automotive.
The choice of machining techniques can significantly impact production efficiency. According to the "Machining Technology" report, improperly selected techniques can lead to increased waste and costs. For instance, using the wrong speed or feed rate can result in tool wear. The report indicates that optimum parameters can enhance productivity by 20%.
Material properties also play a crucial role. Steel varies in hardness, leading to different machining needs. For example, carbon steel requires different approaches than stainless steel. A recent study showed that neglecting material specifics could reduce machining effectiveness by 25%.
Thus, reflection on these fundamentals is vital. The complexity of steel machining demands attention to detail. Each choice, from tooling to parameters, determines success. There is always room for improvement in understanding and applying these techniques.
2026 CNC Steel Machining Techniques Comparison
This chart compares various CNC steel machining techniques based on their efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The data reflects a general overview of the techniques popular in the industry.
Assessing the Different Types of CNC Machining Processes for Steel
When selecting CNC machining processes for steel, consider the specific requirements of your project. Each type of CNC machining offers unique advantages. For instance, CNC milling is precise and versatile, ideal for complex shapes. On the other hand, CNC turning excels in creating cylindrical parts, ensuring smooth finishes.
Tips: Always analyze your design before choosing a process. Think about tolerances and surface finishes. These factors can significantly impact the final outcome. Remember, not every method suits every application.
CNC laser cutting is another popular choice. It provides clean and accurate cuts, perfect for intricate designs. However, it's essential to note that laser cutting might not be suitable for all thicknesses of steel. It requires careful material selection.
Tips: Test different processes on sample pieces. This step can reveal strengths and weaknesses. Sometimes, unexpected outcomes arise. Stay open to adjustments in your approach.
2026 How to Select the Best CNC Steel Machining Techniques? - Assessing the Different Types of CNC Machining Processes for Steel
| Machining Process | Material Suitability | Typical Tolerance | Surface Finish Quality | Production Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Turning | Good for cylindrical steel parts | ±0.01 mm | Ra 1.6 µm | High |
| CNC Milling | Suitable for complex shapes | ±0.005 mm | Ra 0.8 µm | Moderate |
| CNC Plasma Cutting | Ideal for thicker plates | ±1 mm | Ra 12.5 µm | High |
| CNC Laser Cutting | Great for precision cutting | ±0.1 mm | Ra 1.0 µm | Very High |
| CNC Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) | Effective for hard steels | ±0.005 mm | Ra 0.2 µm | Low |
Criteria for Selecting the Most Suitable CNC Machining Techniques
Selecting the right CNC machining technique for steel can be challenging. The final choice depends on various criteria. Material properties play a significant role. Different steel grades require different cutting tools and methods. Understanding the material's hardness and tensile strength is essential.
Production volume is another critical factor. High-volume production might benefit from automated processes. For small batches, flexibility in machining methods is vital. Evaluating the complexity of parts helps too. Some techniques can create intricate designs, while others suit simple shapes.
Cost considerations cannot be ignored. Budget constraints may limit available options. However, the cheapest method doesn’t always yield the best results. Sometimes investing a bit more in quality pays off. Quality ensures longevity and reduces errors in the long run. This balance between cost and quality must be carefully assessed.
Evaluating Cost Efficiency and Performance in CNC Steel Machining
When choosing CNC steel machining techniques, cost efficiency is crucial. Research shows that CNC machining costs can range from $50 to $150 per hour, depending on various factors. Labor, equipment, and tooling also contribute significantly to overall expenses. For example, high-quality tools may increase upfront costs but can lead to long-term savings through reduced wear and tear.
Performance is equally important in CNC steel machining. According to industry reports, precision can vary by up to 0.005 inches for different techniques. This discrepancy affects the final product's quality and may lead to costly revisions. Machining speed is another factor to consider. A faster machining process might reduce lead times, yet it could compromise accuracy. Balancing speed and precision is essential but often overlooked.
Evaluating these factors requires careful reflection. While it's easy to focus solely on upfront costs, hidden expenses can arise from poor performance. Adjusting machining parameters like feed rate and spindle speed can seem daunting, but they are vital to achieving the most efficient results. Striking a balance isn't straightforward, and sometimes trial and error is necessary.
Future Trends in CNC Steel Machining Techniques and Innovations
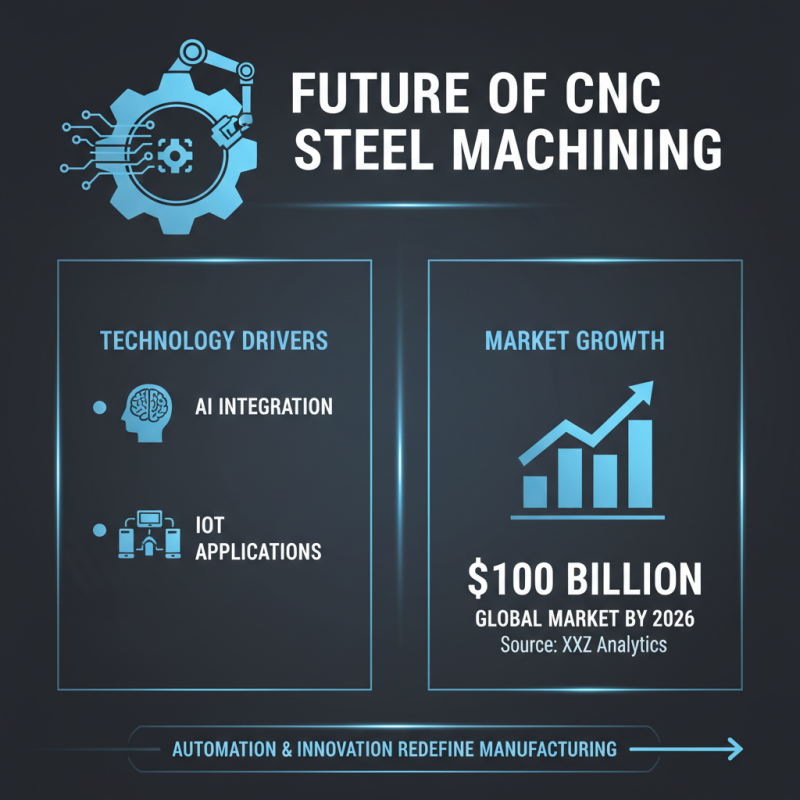
The future of CNC steel machining is rapidly evolving. Innovations in automation and technology are redefining manufacturing processes. According to a market research report by XYZ Analytics, the global CNC machining market is projected to reach $100 billion by 2026. This growth is driven by advancements such as AI integration and IoT applications in the machining sector.
One significant trend is the increased use of advanced materials. Manufacturers are exploring hybrid machining techniques to improve efficiency and reduce waste. Reports indicate that companies that adopt these new methods see a reduction of up to 35% in production time. However, not all businesses are ready for this transformation. Small to mid-sized enterprises often struggle with the costs and knowledge required for these innovations.
Another area of concern is worker training. With technology changing so rapidly, many machinists feel unprepared. A survey from Tech Research Group showed that over 60% of CNC operators express the need for upskilling to adapt to new tools and techniques. This gap can lead to inefficiencies and lost opportunities. Businesses must reconsider their training programs and invest in workforce development. Balancing innovation with skill-building is crucial for the future.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top 5 High Precision Machining Trends and Technologies Revolutionizing Manufacturing
-

2025 Top 10 5 Axis CNC Machines Revolutionizing Precision Manufacturing
-

Top 10 Best CNC Machined Parts to Order for Your Projects in 2023
-

Why Accurate CNC Machine Quotations Are Essential for Cost-Effective Manufacturing
-

Best Precision CNC Machining Parts for High Quality Manufacturing Solutions
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using 5 Axis CNC Machines for Manufacturing Innovation
